Welcome to Quantum Sensor Optimization’s documentation!
qsensoropt is a framework that has been created
to automate a broad class of optimizations that can be found in the
tasks of quantum parameter estimation, quantum metrology and
quantum hypothesis testing. It works both for Bayesian estimation
as well as for point estimation. qsensoropt is based
on model-aware Reinforcement Learning with policy gradient.
Getting Started
Overview
qsensoropt is a framework written in Python
and based on Tensorflow. Its typical use case is to train
a neural network to optimally control a quantum sensor.
The framework is based on the interaction of the three classes
that are
PhysicalModel,
Simulation,
and
ParticleFilter.
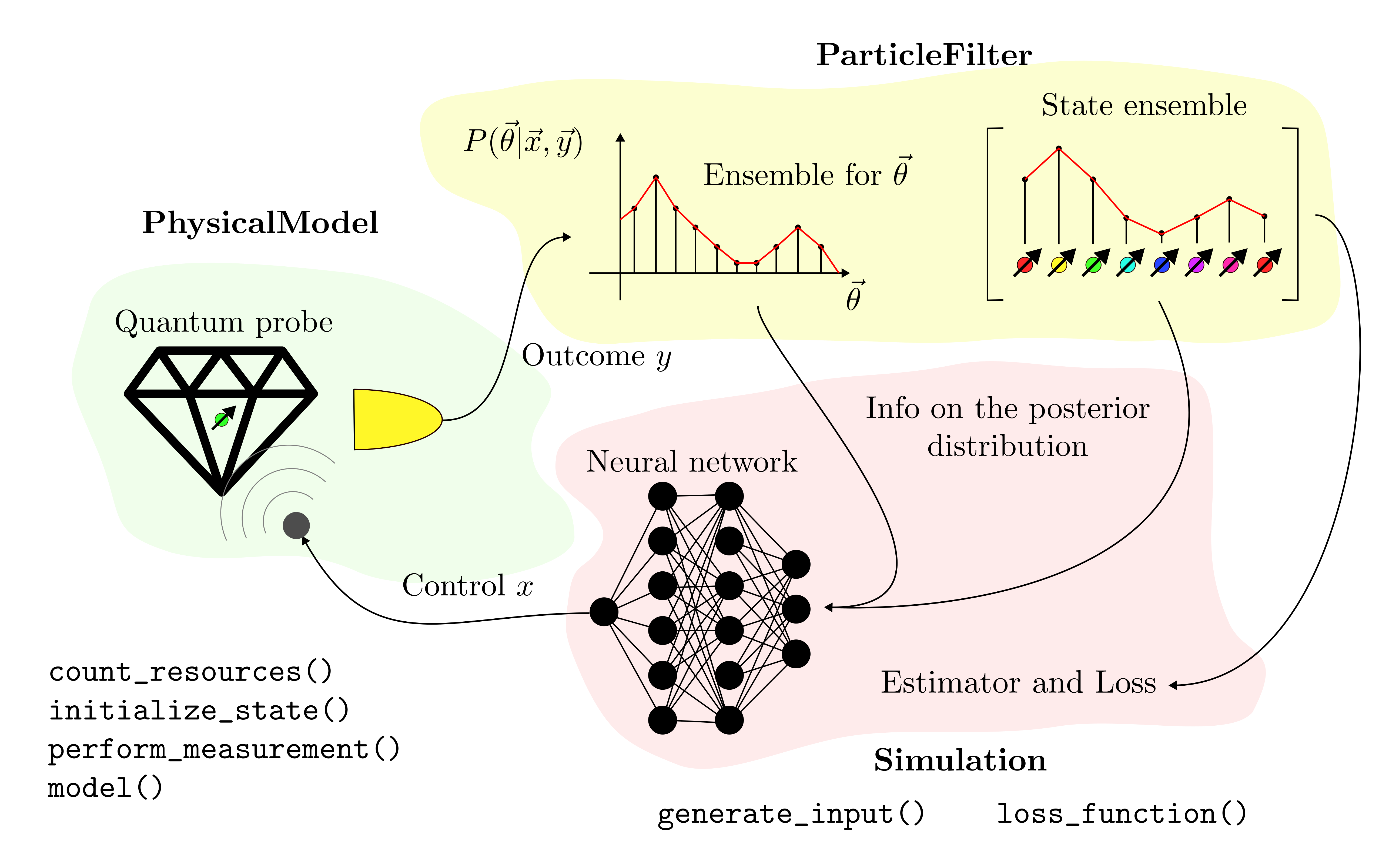
The user is required to create a new class with the description
of the quantum probe that inherits either from
StatefulPhysicalModel
or
StatelessPhysicalModel
according to whether the probe is stateless (meaning that its state
is reinitialized after each encoding and measurement) or stateful
(the measurements affect each other through the quantum backreaction
on the probe). In this class the user must define the methods
count_resources(),
perform_measurement(),
model(),
and
initialize_state()
(this last one is only needed if the model is stateful).
If the system model is not representable analytically in a compact form, it it possible to use a neural network that has been calibrated to reproduce the statistics of the physical system, thereby implementing both applications of machine learning to quantum metrology that have been described in the literature 0.
Having specified the physics of the probe
the user is now asked to define a class
specifying how the particle filter should
interact with the neural network and what is
the error in the metrological task. This is
done by deriving either the class
StatefulSimulation
or
StatelessSimulation
and by implementing the two methods
generate_input()
and
loss_function().
If the users tasks
is a typical quantum metrological problem, where the loss
is the Mean Square Error, and where we want the neural network
to produce the optimal control based on the first and
second moments of the particle filter,
then it is possible to use directly the classes
StatelessMetrology
or
StatefulMetrology
for the simulation, without the need of defining a
new class.
At this point we are ready to instantiate the classes created, passing to the constructors the parameters to tune the estimation.
At this point having specified the details of the
physical model and of the simulation, the user is ready
to instantiate the two define class and the
ParticleFilter. Calling then the function
train() on the simulation will
train the network in controlling the sensor, while
the function performance_evaluation()
evaluates its performances
- 0
Advanced Photonics, Vol. 5, Issue 2, 020501 (March 2023).
API documentation
All of the APIs are documented here
Examples
Several examples can be found in this repository
Acknowledgement
We gratefully acknowledge computational resources of the Center for High Performance Computing (CHPC) at SNS.